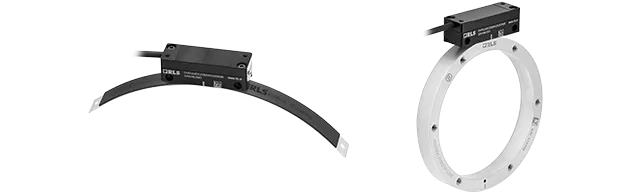
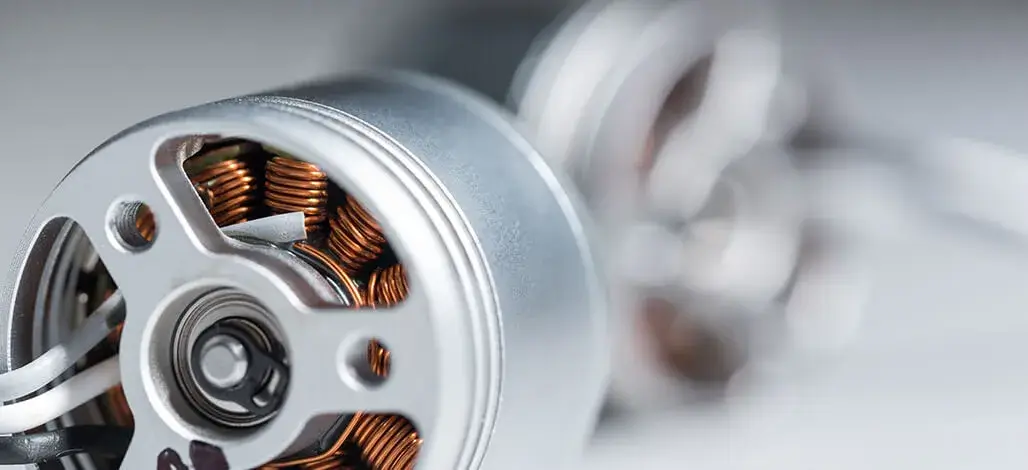
Electric motors
RLS is strongly rooted in drive technology and has been developing advanced sensor solutions for speed and position detection (commutation) for various electric drives for decades.

"The variety on the market is huge, we needed the best technology that would fit into our motors. RLS were happy to adapt and tailor their existing magnetic encoder products to our needs." TQ-RoboDrive (Germany)
Many drive manufacturers trust our OnAxis encoders, as well as bearingless encoders like RoLin, AksIM and Orbis. They are all based on highest quality, robustness and sustainable technologies. We are also happy to accept individual challenges and realize modifications and special solutions.
How do encoders in electric motors work?
Brushless motor
Challenge:
Built-in rotary encoders are used to indicate the angle of the motor shaft in brushless permanent magnet motors. In such cases, the encoder serves as a feedback device, which is crucial for the proper operation of the equipment. Brushless motors require electronic commutation, often partly achieved by using rotor magnets as low resolution absolute encoders (typically six or twelve pulses per revolution). The resulting shaft angle information is transmitted to the servo drive so that it can excite the correct stator winding at any time.
Solution:
For the BLDC motor to function properly, the controller (drive) must know the position of the rotor. To achieve this, zeroing should be carried out. Zeroing is a process in which an alignment of the electrical and mechanical position is achieved. In this way the controller knows through which winding a current should be sent.
SPEED
Speed detection can be achieved with incremental encoders, from compact encoders such as RMBs, RMs, to bearingless encoders such as RoLin or AksIM, as well as redundant and space-saving solutions. We are also happy to implement modifications and special solutions.
POSITIONING
A servomotor is a closed-loop servo mechanism that uses position feedback to control its movement and end position. For this application, absolute encoders like AksIM or Orbis are mainly used. The input to its control is a signal (either analog or digital) representing the commanded position for the output shaft. The motor is paired with a type of encoder to provide position and speed feedback. The measured position of the output is compared with the commanded position, the external input to its control. If the output position deviates from the target position, an error signal is generated which then causes the motor to rotate in both directions to bring the output shaft to the corresponding position. As the positions approach, the error signal is reduced to zero and the motor stops.
Why RLS magnetic encoders?
Industry Challenges
- Reliability
- Repeatability
- Low weight and compact size
- Low energy consumption
RLS Solutions
- Good price-performance ratio
- Wide range of available sizes
- Wide range of resolutions
- Industry standard absolute or incremental output options
- High dynamic response
- High accuracy
- Large installation tolerances
- High reliability
- Non-contact 360° rotation or linear position detection
- Low power consumption
- Immune to stray external magnetic fields
Success Stories
Recommended products
-

AksIM-4™ Hiperface DSL off-axis rotary absolute magnetic encoder
-

FlexAB™ Absolute Magnetic Scale System for Large Diameters
-

AksIM-4™ Big Rings Off-Axis Rotary Absolute Magnetic Encoder
-

FlexIN™ Magnetic Scale System for Large Diameters
-

RM08 Miniature Rotary Magnetic Encoder
-

RMB14 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module
-
![RMB20 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module with AM4096 chip]()
RMB20 with AM4096 chip Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module with AM4096 chip
-
![RMB20 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module]()
RMB20 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module
-
![RMB23 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module]()
RMB23 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module
-
![RMB28 / RMF44 / RMF58 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module]()
RMB28 / RMF44 / RMF58 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module
-
![RMB28 / RMF44 / RMF58 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module]()
RMB28 / RMF44 / RMF58 with AM4096 chip Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module with AM4096 chip
-
![RMB28 with SATI03 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module]()
RMB28 with SATI03 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module
-
![RMB29 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module]()
RMB29 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module
-
![RMB30 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module]()
RMB30 Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module
-
![Orbis™ Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module]()
Orbis™ Rotary Magnetic Encoder Module
-
![LA11 Linear Absolute Magnetic Encoder]()
LA11 Linear Absolute Magnetic Encoder
-
![AksIM-2™ Off-Axis Rotary Absolute Magnetic Encoder Module]()
AksIM-2™ Off-Axis Rotary Absolute Magnetic Encoder Module
-
![MB039-R]()
AksIM-2™ Redundant Off-Axis Rotary Absolute Magnetic Encoder Module
-
![LinACE™ InAxis Linear Absolute Magnetic Shaft Encoder]()
LinACE™ InAxis Linear Absolute Magnetic Shaft Encoder
-
![RLC2IC Miniature Incremental Magnetic Encoder Module]()
RLC2IC Miniature Incremental Magnetic Encoder Module
-
![HiLin™ High-accuracy Linear Magnetic Encoder System]()
HiLin™ High-accuracy Linear Magnetic Encoder System
-
![Orbis™ Housed Through-hole Rotary Encoder]()
Orbis™ Housed Through-hole Rotary Encoder
-
![LA12 Absolute Magnetic Encoder System with Mitsubishi, Yaskawa and Fanuc Serial Communication]()
LA12 Absolute Magnetic Encoder System with Mitsubishi, Yaskawa and Fanuc Serial Communication
-
![RLB Miniature Incremental Magnetic Encoder Module]()
RLB Miniature Incremental Magnetic Encoder Module
-
![RLC2HD Miniature Incremental Magnetic Encoder Module]()
RLC2HD Miniature Incremental Magnetic Encoder Module
-
![RLM Miniature Incremental Magnetic Encoder]()
RLM Miniature Incremental Magnetic Encoder
-
![AksIM™ Off-Axis Rotary Absolute Magnetic Encoder]()
AksIM™ Off-Axis Rotary Absolute Magnetic Encoder